POSTPARTUM DEPRESSION (PPD)
A DEEPER LOOK AT POSTPARTUM DEPRESSION: SYMPTOMS, CAUSES, AND OVERCOMING STRATEGIES
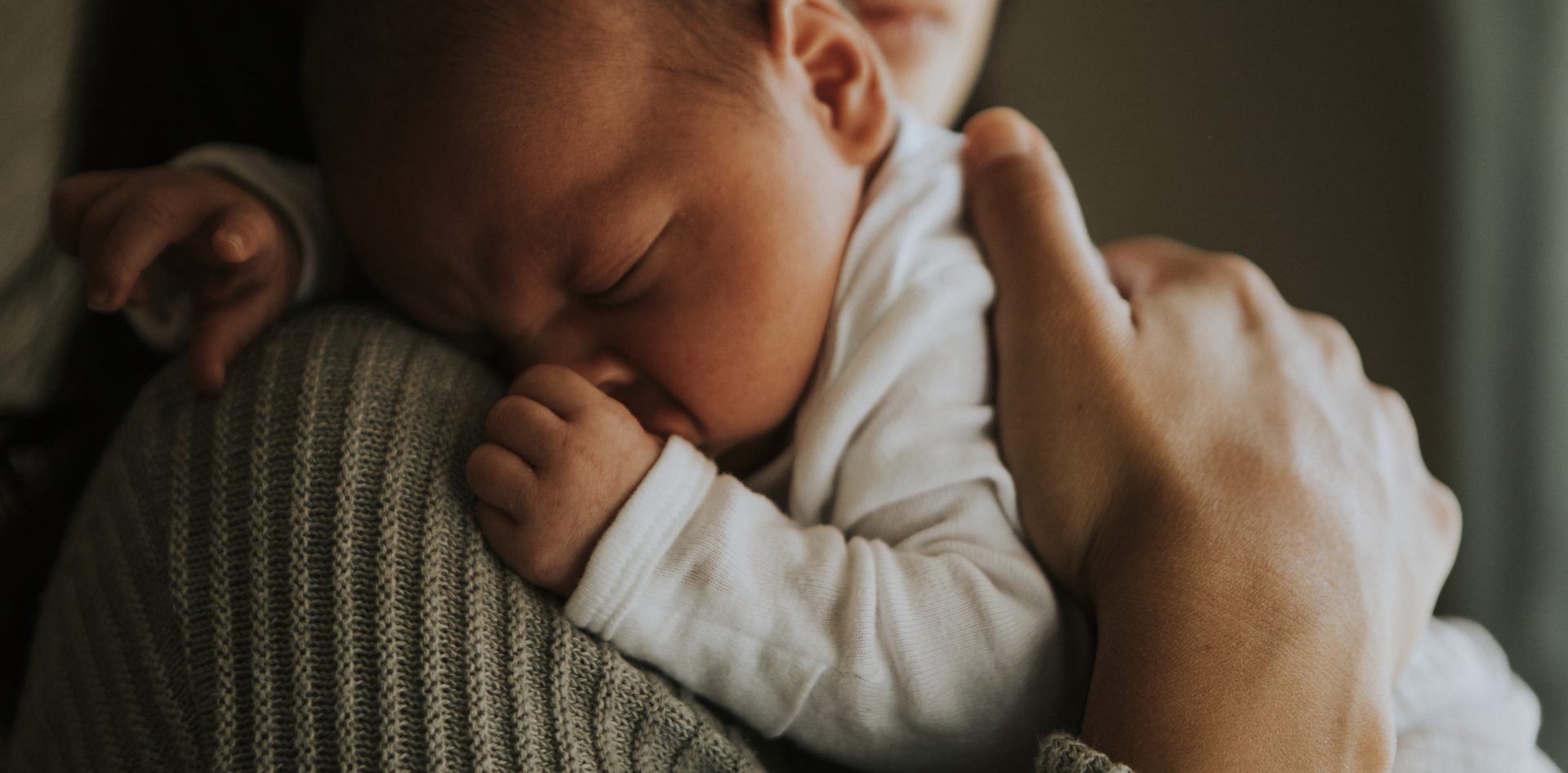
Postpartum Depression (PPD) is a severe form of depression that can impact women after childbirth. However, this mood disorder may be attributed to hormonal fluctuations, physical changes, and the emotional upheaval associated with new parenthood. We’ll delve deeper into PPD, exploring its symptoms, risk factors, treatment alternatives, and preventative measures.
UNDERSTANDING THE SYMPTOMS
PPD can manifest through a broad spectrum of symptoms, varying from mild to severe. Common symptoms may include:
- Persistent Feelings of Sadness or Worthlessness: Women with PPD often struggle with constant feelings of sadness, despair, or worthlessness that seem difficult to overcome.
- Fatigue or Lack of Energy: Extreme exhaustion or an unexplained lack of energy, far beyond the usual ‘new mom fatigue,’ is often experienced.
- Sleeping Issues: Affected women might struggle with insomnia or oversleeping, making it hard to maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Changes in Appetite: PPD can bring about significant changes in appetite, therefore, leading to unexplained weight gain or loss.
- Difficulty Concentrating or Making Decisions: Women might find it challenging to concentrate or make even mundane decisions,therefore, affecting their day-to-day functioning.
- Anxiety and Excessive Worry: An overwhelming sense of fear and anxiety, often centred around the baby’s health or parenting abilities, is a common manifestation of PPD.
- Social Withdrawal: Women might distance themselves from family and friends, indicating a struggle with PPD.
UNPACKING THE RISK FACTORS OF POSTPARTUM DEPRESSION
Understanding the risk factors for PPD can equip us better to prevent and manage it. However, several other factors may raise the chances of developing PPD:
- Personal or Family History of Depression: A personal history of depression or mood disorders or a family history of mental health issues can increase PPD’s risk.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: The dramatic shift in hormonal levels during and after pregnancy can trigger PPD.
- Stressful Life Events: Women facing significant life stressors during pregnancy or after childbirth. These stressors include financial instability or lack of social support, are more susceptible to PPD.
- Childbirth Complications: A complicated childbirth experience or a sick baby may elevate the risk of PPD.
- Inadequate Coping Mechanisms: Poor stress coping strategies may leave women more vulnerable to PPD.
- Unrealistic Expectations: A discrepancy between reality and expectations about motherhood can often contribute to PPD.
NAVIGATING TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR POSTPARTUM DEPRESSION
Successfully managing PPD often involves a multi-faceted approach. Additionally, other approaches includes psychological therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications:
- Psychotherapy: Therapy sessions involving Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Interpersonal Therapy (IPT). These sessions help women navigate PPD by developing coping strategies and addressing negative thought patterns.
- Medication: Antidepressants, such as Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), can help regulate mood and manage PPD symptoms.
- Hormone Therapy: If hormonal imbalances trigger PPD, hormone therapy might help alleviate symptoms.
- Support Groups: Participating in support groups can provide women with a safe space to share experiences, learn from others, and find encouragement.
- Lifestyle Changes: Incorporating regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can improve overall mental health and wellbeing, aiding PPD recovery.
ADOPTING PREVENTIVE STRATEGIES
While PPD may not be entirely preventable, adopting specific strategies can help reduce its risk and severity:
- Prenatal Care: Regular prenatal check-ups can ensure physical health and provide an opportunity to discuss any emotional concerns or anxiety about motherhood.
- Strong Support System: Having a network of supportive family and friends can provide emotional and practical assistance during this transformative phase.
- Prenatal Classes: Undoubtedly attending prenatal classes can help women prepare for childbirth and understand the realities of parenthood.
- Self-care: In addition to engaging in relaxation activities, maintaining physical health, and pursuing hobbies, manage stress and maintain emotional wellbeing.
Postpartum depression is a significant mental health concern impacting many women after childbirth. Recognizing symptoms, understanding risk factors, exploring comprehensive treatment options, and adopting preventative strategies are vital for navigating this complex condition. With the proper intervention and support, women with PPD can fully recover, leading to a healthy, fulfilling life with their newborns.